DAZZLE: Drone-Acquired Zebra data for
Large-scale Ecology research
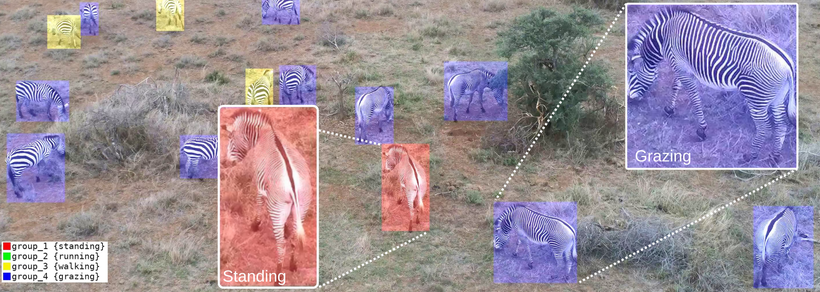
DAZZLE Dataset consists of semi-automatically labeled behaviors of plains and Grévy's zebras holistically for all individuals
in complete scenes, in addition to bounding boxes on individual animals. DAZZLE has >30K frames and >160K annotations.
Dataset Contents
- Extracted image frames from the video and corresponding annotations.
- Generated dataset for the zebra detector training, merged with MSCOCO
- Generated dataset (training, test1, test2) for classifier training and testing.
- Weights of the final trained zebra detector network.
- Weights of 10 trained behavior networks, each with a different seed.
- Videos: 24
- Frames: 30627
- Zebras: 258
- Total Annotations 162799, Of those -
-
- grazing: 71734
- standing: 33896
- walking: 43235
- running: 13934
Acquisition Equipment
All videos in the dataset were recorded using four off-the-shelf drones: 2 DJI Mavic 2 Pro and 2 Parrot Anafi 4K. Videos from Mavics were recorded at 4K resolution (3840x2160 pixels at 29.97 fps). Videos from Anafis were also recorded at 4K resolution (4096x2160 pixels at 23.98 fps).
Acquisition Location
A region in Kenya characterized by arid and semi-arid savannahs and woodlands.
Acquisition Date and Time
All videos were recorded during daytime (between 0800 & 1800 local time), in the months of July and August 2022.
Acquisition Procedure
The research team first searched for the presence of zebra herds through manual observation from an off-road vehicle. After spotting the zebras, which typically happened during the first hour of the search, the vehicle was stopped approximately 200 m from the herd. One or two drones were then manually deployed such that the take-off sound did not startle the herd; the drones were placed behind the vehicle, on the opposite side of the zebra herd. After take-off, the drones quickly ascended to an altitude of approx. 100 m. From there, they were cruised, at a relatively constant altitude, towards the center of the herd, and then slowly descended up to approx. 10-20 m above the herd. This procedure was performed by the drone pilot by manually observing the drone and the zebra herd, simultaneously. Once the drones reached close to and above the zebras, they were flown following the zebras, keeping as many zebras as possible in their cameras' field of view. To this end, the pitch angle of the camera gimbal and the yaw orientation of the drone were manually controlled by the pilot. While the drone cameras did not have any optical zoom, digital zoom was also never performed. Even during the period of approach (ascend and initial cruise), the pilot attempted to keep the animals in the drone camera's field of view, however this was not always successful. The drones were kept following the herd until the battery levels approached a pre-determined threshold to return safely. At that point, the drones were manually flown back to the start position, near the vehicle. A complete flight was approx. sim 25 minutes, out of which the useful video recordings range from 5 to 20 minutes.